Answer:
Ferdinand de Saussure is known as the founder of general linguistics and one of the most influential figures in modern linguistics. He was born on November 26, 1857, in Geneva, Switzerland. He stood as a notable Swiss linguist, philosopher, and semiotician during the 20th century. He played a very important role in the development of linguistic research in that era.
According to him, linguistics is a branch of the general science of signs which he proposed to call ‘semiology’, now commonly known as ‘semiotics’. After his passing, his students Charles Bally and Albert Sechehaye published the book ‘Course in General Linguistics‘ in 1916, which became one of the seminal works in linguistics of the 20th century.
Saussure’s ideas in his book propose that language can be studied as a structured system of differences, separate from the messy dialectics aspects of real-time production and comprehension. He also made important contributions to ‘Indo-European philology’, which led to the ‘Laryngeal Theory’. His work laid the foundation for Structuralism by creating a way to make educated guesses about unknown language features based on what’s known.
Saussure’s influence resulted in two major linguistic theories.
In America, Leonard Bloomfield developed ‘distributionalism’, partly inspired by Saussure. Saussure’s ideas also had a significant impact on “Systematic Functional Linguistics”.
In Europe, the Prague School, represented by Nikolay Trubetzkoy and Roman Jakobson, expanded on his ideas. Jakobson applied Saussure’s concepts to create a broader theory of how language sounds work.
However, Saussure’s influence extended beyond linguistics to other fields. His structuralism theory inspired various thinkers, like Ronald Barthes and Jacques Lacan, who applied it to philosophy, psychoanalysis, anthropology, and more.
Concept of Langue and Parole:
According to Saussure, ‘language is a system of signs that express ideas’. He split it into two parts: “langue,” and “parole,”. Langue and Parole is a French word.
Langue: It refers to “the abstract system of language”.
Parole: It refers to speech or the “putting into practice of language”.
Saussure thought of language as a social product instead of simply being a natural organism. So it is not a function of the speaker but is passively assimilated and the act of speaking is premeditated.
Also some more of his contributions:
- Synchrony and Diachrony: Saussure introduced the terms “synchronic” and “diachronic”. Language when studied synchronically is taken as a complete system at a given point in time. When it is studied diachronically, it is about historical developments.
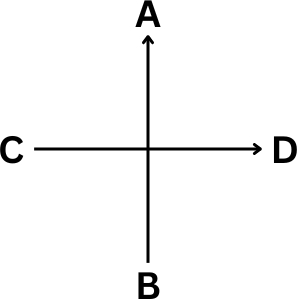
Here the AB axis refers to the synchronic axis which means “studying the language at a given point in time.” On the other hand, the CD axis refers to the diachronic axis which is the historical development.
- Signifier and Signified: Saussure introduced the idea of a linguistic sign being composed of two inseparable parts: the “signifier” (the sound pattern) and the “signified” (the concept or meaning). This concept laid the foundation for semiotics, the study of signs and their meaning in various contexts.
- The Arbitrariness of the Sign: Argued that the relationship between the signifier and signified is arbitrary, challenging the idea of natural connections between words and meanings.
- Syntagmatic and Paradigmatic Relations: Introduced the concepts of how linguistic units combine in sentences (syntagmatic) and how they can be substituted for one another (paradigmatic).
- Influence on Semiotics: Laid the foundation for the study of signs and their meanings in semiotics.
- Shift to Structuralism: Initiated the structuralist approach to analyzing systems of meaning in language and culture.
- Legacy in Modern Linguistics: His ideas continue to influence modern linguistics, emphasizing systematic language analysis and context.
- Critique of Historical Comparative Linguistics: Reevaluated language change within a synchronic and diachronic framework.
So lastly, we can say that, Saussure and his great contributions collectively reshaped the study of linguistics and paved the way for new perspectives on language structure, meaning, and interpretation.